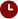
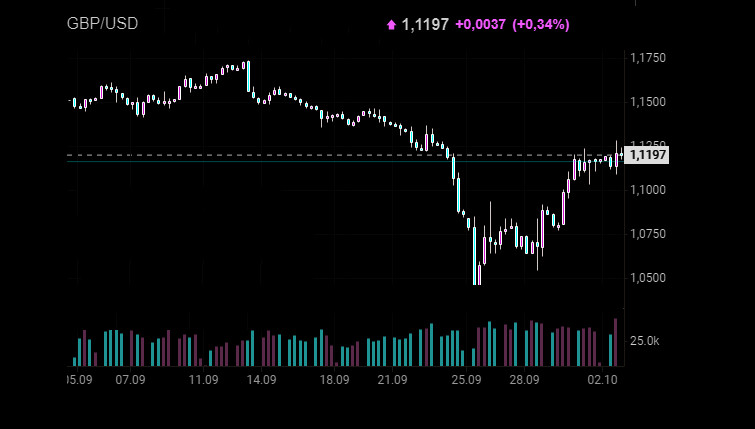
The British pound has recouped almost all of its losses after a rapid fall last week. Does it mean that the pound is back on track? Not necessarily.
GBP's rise likely to be short-lived
Once Liz Truss said that she prepared to be unpopular. It seems that she already is, especially when taking into account the reaction of financial markets. The plunging pound sterling combined with rising bond yields wreaked havoc in the market, or rather to a "submerging market" as Larry Summers called it. Two weeks after Queen Elizabeth II's funeral, the UK has returned to what now seems to be the "new normal" - a transition to a new crisis.
Last week, UK's Chancellor of the Exchequer Kwasi Kwarteng promised to introduce a new plan and a set of reforms to deal with public debt and other issues. What is more, he assured policymakers that his budget statement planned for November 23 will include an independent analysis by the Office for Budget Responsibility.
Meanwhile, the Bank of England said there was no need for an emergency meeting. Yet, the regulator pledged to do its best to tackle inflation. However, none of these announcements could calm down the markets. The pound lost nearly 0.6 pips in September, having reached the level of 1.03 at one point. What is the reason behind this collapse?
First of all, market participants may have overreacted. The global economy is indeed on the edge of a recession. But when it comes to the UK, it doesn't seem that bad. For instance, the UK has the lowest debt-to-GDP ratio in the G7, while its fiscal policy does not differ much from that of other developed countries. The only surprising move was the decision to abolish the 45% income tax rate. So, Great Britain seems the only country that can potentially withstand the pressure from the US dollar. So, what's the problem?
At first glance, such a negative reaction could be caused by the idea that this will be a game changer for the economy. This statement may be too general, though, as most of the tax cuts will simply return the rates to the levels recorded in 2019. Therefore, the panic that broke out in the market seems to be caused by the lack of any focus on financial stability and a sole priority given to tax cuts. In other words, markets did not get enough confirmation to start the bullish run. A tax reduction was perceived as a dovish signal which could be followed by more rate cuts and a deepening recession. But in fact, there is no drastic change in the fiscal policy.
Some analysts compared this move to hitting the brake and gas at the same time. The current fiscal policy is loose while the monetary policy is tight. Yet, Liz Truss and her team insist that this is a special step rather than a mistake. Obviously, she used fiscal and monetary policies as a carrot-and-stick approach aimed at easing the pressure on manufacturers. Meanwhile, the central bank was meant to curb inflation in financial markets with higher interest rates in order to bring the yield curve back to normal.
An increase in interest rates was a widely expected step.
On the other hand, tax cuts also look like a reasonable step amid the energy crisis that is supposed to help the real sector. It is also true that taxation and spending should go in hand with a supply-side reform which may boost the growth potential of the economy. However, the Parliament doesn't agree with this statement.
The economic measures proposed by Liz Truss sparked a heated debate and a lot of criticism among UK policymakers. Senators insist that lower taxation will affect the budget which means that public debt will bloat. This is what the Labor Party would like to avoid at all costs.
Unfortunately, this cost may turn out to be too high for a producer. Pressured by soaring energy prices, rising wages, expensive commodities, and high taxes, producers will inevitably cut production and raise prices, which will only fuel inflation in the long term.
It would be wiser to cut budget spending on unnecessary programs and try to take the most of what we have. Yet, this scenario will definitely cause public disapproval.
Therefore, the approach based on "save money and support producers" seems the most suitable now. The problem is that the new Prime Minister promises not to save but to show growth which sounds alarming.
Conservatives believe that tax cuts are not the right way to deal with the problem. They are sure that these measures will spur demand, accelerate inflation, and eventually force the Bank of England to introduce more rate hikes to offset the side effects of lower taxes.
But that's not all.
UK market faces capital outflow
There is another issue concerning the current account deficit which includes the UK trade balance and the net income from foreign investment and transfers. It has recently deteriorated to a record 8.3%, confirming the joke that Britain's balance of payments shortfall will leave it reliant on the "kindness of strangers".
The UK proclaimed itself a new financial hub after Brexit. This brought good profits to the Treasury while the market stayed bullish. But when the situation changed, a natural flight of capital began – investors fled from risk assets to safe-haven assets. With this in mind, the country had to pay dearly for its reliance on the stock market. So, will the UK stay a good choice for investors or will they continue to avoid this market sector?
The combination of a sliding pound and higher interest rates can make the UK market more attractive to investors. This would help the UK cover its huge external deficit. At the same time, this combination slows imports and supports exports, thus narrowing the gap between them. The current account deficit of the UK has always been stable which is why we can suggest that it is resilient to changes in the exchange rate.
This sounds well in theory. In practice, the policy of central banks gives different results which makes traders more doubtful.
So far, the UK market has been popular among investors as they used to trust British financial institutions. Moreover, the UK's net international investment position is improving when the pound is weak. Yet, the recent events have proved how fragile the UK economy can be and how quickly the trust can be ruined. This is especially true for the financial sector while the shares of large manufacturers are still in good shape.
It should be noted that the highest tax rate of 37% in the US accounts for around $539,900 (£504,681.65), while a 40% tax rate in the UK stands for just over £37,700 ($39,475.30). So, all these tax cuts will not make Britain a low-tax haven. Will they change the spending or investment habits of citizens?
Undoubtedly they will. Now is the time for rigid accounting and saving every penny. However, those who invest most of their funds - the wealthy investors - may act differently. Lowering taxes for the rich seems to be the least effective way to stimulate demand in the economy. Economists say that the marginal prosperity to consume (MPC) of wealthy citizens is lower than that of the poor. In other words, this extra money left from reduced taxes will be saved, not spent. This is actually good for the UK economy as these funds will be taxed as well.
Liz Truss's controversial plan raises too many questions
First of all, rental costs are still a big concern for households.
Higher mortgage rates may offset all the benefits of lower taxes for households. This factor may in turn influence the housing market.
If the moves in risk-free interest rates that we have seen in response to the mini-budget stick, many households will find they are worse off as their mortgages roll over and the bill skyrockets. The shift towards fixed rate mortgages in the UK means that it may take some time to overcome some challenges. Around 20% of mortgages have a variable rate. But when it does finally bite, homeowners, particularly those with elevated debt-to-income ratios, will see their mortgage bill surge.
Then, there is a huge sector that requires constant spending - the health care system.
It is hard to imagine how the UK can have a meaningful supply-side revolution with a completely taxpayer-funded universal health-care system whose needs are growing all the time as the population ages and as health care becomes more complex and expensive. In fact, we're seeing the NHS failing a number of key targets — not to mention social care, which remains fragmented and underfunded. Can the economic plan proposed by Liz Truss succeed if the NHS is failing?
This seems to be a serious challenge. If Liz Truss wants to cut taxes and show that she is still serious about fiscal discipline, she needs to cut expenditures too. But spending surged during the Covid crisis and is likely to hit a new higher level.
If tax cuts need to be accompanied by spending reductions, it is very hard to argue that you are focusing solely on growth because you are taking with one hand and giving with another. So, probably, to make the plan viable, Liz Truss will have to reduce spending.
There are also growing concerns among UK citizens about keeping their jobs amid inflation and higher immigration flows. The workforce is likely to grow more quickly with a looser immigration regime and that will bridge some of the gap between the economy's current trend rate of growth and where Kwarteng - the main advocate of the new plan - would like this growth to be. Actually, this is not so bad: it could perhaps add 0.2 percentage points to annual growth, which still leaves around a percentage point to make up.
What does the Labour Party offer?
Labour leader Keir Starmer has made clear he'd reverse the cut to the top rate of tax and impose bigger windfall taxes on energy companies. This would be a direct blow to the real manufacturing sector.
It is also not clear whether the markets would be calmer about the Labour government and whether businesses can make long-term investment decisions with such changing policy weather.
It is important to understand that markets are calm when there is a credible plan. If Labour came in and demonstrated such a plan, there is no reason to think there would be a negative reaction. Meanwhile, larger producers who lobby for their interests are unlikely to show their support. The main parties of the day should agree on a long-term investment plan for the country, which both parties commit to no matter who is in power.
The market confidence in the UK has deteriorated to such an extent that the Bank of England will have to interfere sooner or later. Any growth cycle in the short term may be offset by another negative reaction of the market.
It was reported today that the UK government has dropped the idea of cutting taxes for top UK earners to avoid criticism from other citizens. This factor has definitely supported the British pound.
The pound has partially recovered from the previous fall mainly thanks to the intervention of the Ministry of Finance. October and November are traditionally considered difficult months for the financial markets. Moreover, debates are still going on about the feasibility of Liz Truss's plan. There even calls for the vote of no confidence in the government, which has only been in power for a month. This factor will weigh heavily on the pound, forcing short-term investors to flee the market.
As we can see, three-month pound-dollar risk reversals, which measure the premium of hedging against a drop in sterling, jumped to the highest since the June 2016 Brexit vote on Friday, signaling that traders anticipate further losses. Analysts predict a further decline as Liz Truss promised to stick to her entire fiscal policy. In her interview with the Telegraph, Truss said she was determined to follow through with her plans for massive tax cuts because she believed they would make the country more successful.
Yet, her plan looks questionable in the long term. If the plan is fulfilled, the UK regulator may record a 0.4% increase in inflation next year. Its impact on growth is even more ambiguous. A weaker pound may stimulate net trade but will not slow inflation which will force the BoE to act. The negative impact may be significant. The Bank of England may hike the rate to 4.25% in the first quarter of 2023, considering the biggest increase of 100 basis points that is planned for November this year. It is not the best idea to make the poor, not the rich, pay in difficult times.
As we can see, Liz Truss has already stepped back under the pressure of public opinion and the senators. There is a risk that her next initiative may also fail.
All these factors make the plan proposed by Liz Truss so attractive among economists. Unless the palm gets more clarity, the British pound will stay a highly volatile currency.